The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external.
Examples supply and demand price floor.
How price controls reallocate surplus.
When price increases by 20 and demand decreases by only 1 demand is said to be inelastic.
Minimum wage and price floors.
Similarly a typical supply curve is.
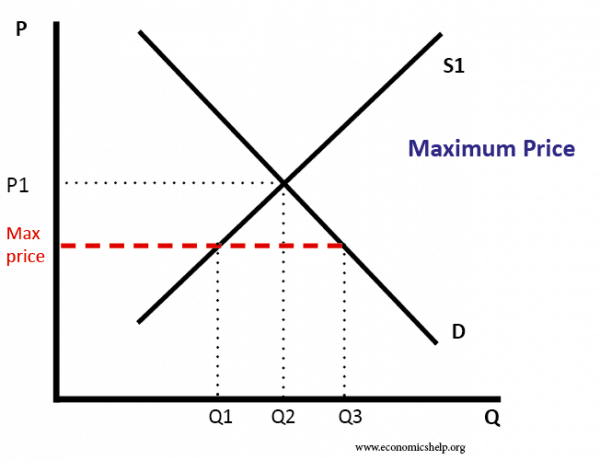
This section uses the demand and supply framework to analyze price ceilings.
Remember changes in price do not cause demand or supply to change.
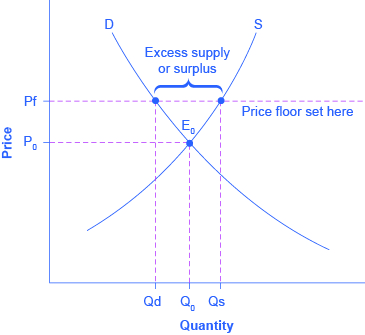
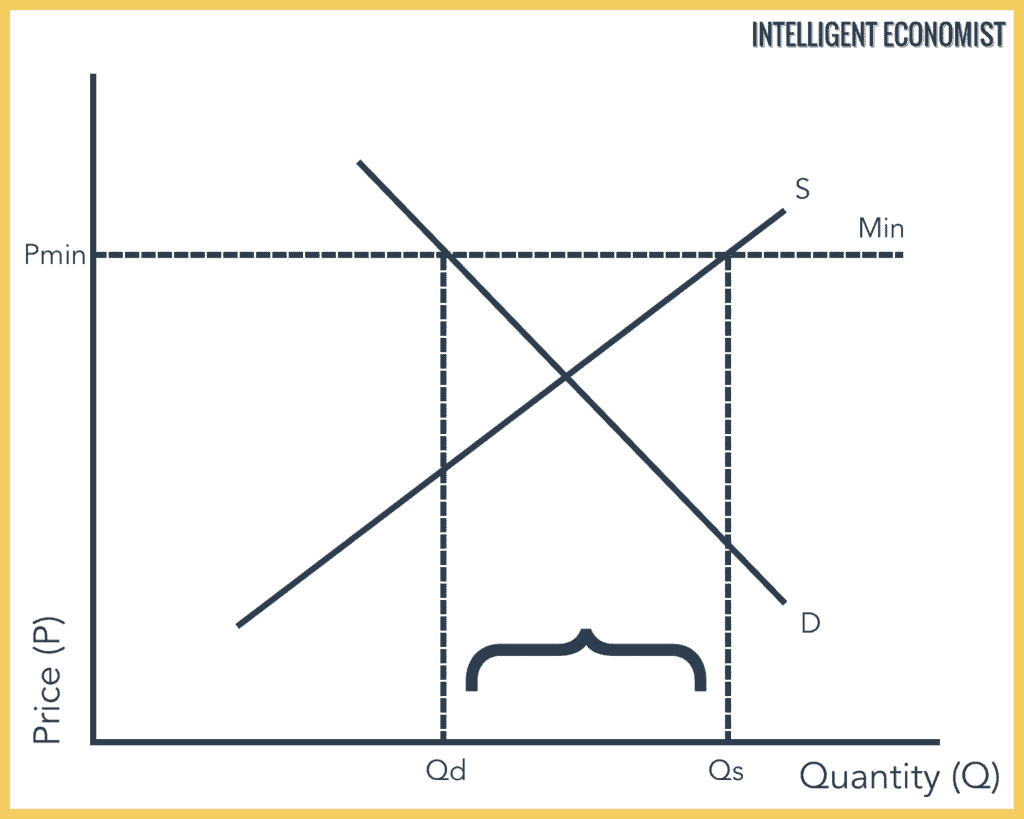
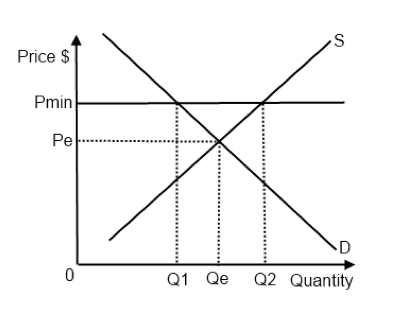
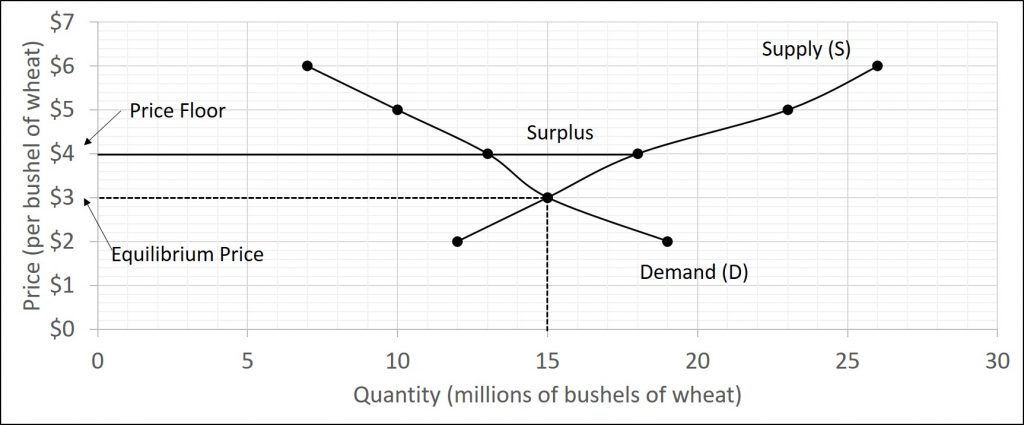
However a price floor set at pf holds the price above e 0 and prevents it from falling.
Demand curve is generally downward sloping which means that the quantity demanded increase when the price decreases and vice versa.
And very low prices naturally.
Draw demand and supply curves for unskilled labor.
Neither price ceilings nor price floors cause demand or supply to change.
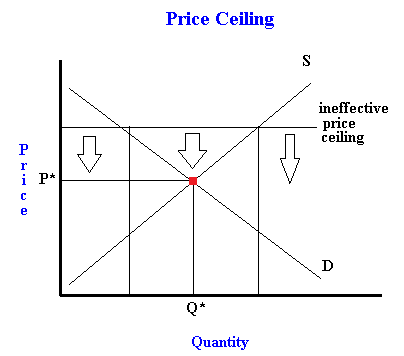
A price ceiling keeps a price from rising above a certain level the ceiling while a price floor keeps a price from falling below a given level the floor.
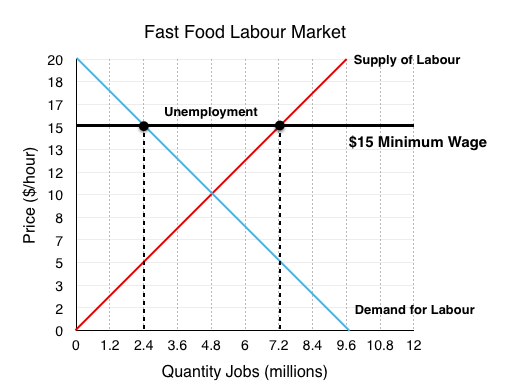
A minimum wage law is another example of a price floor.
A price floor example.
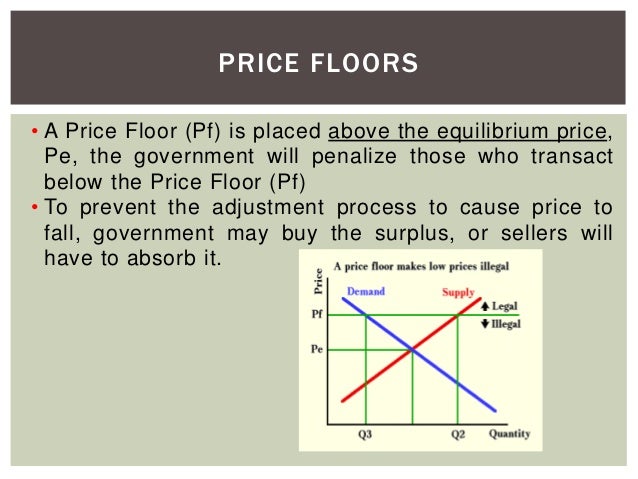
A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service.
The next section discusses price floors.
Taxes and perfectly elastic demand.
The horizontal axis will show the quantity of unskilled labor per period and the vertical axis will show the hourly wage rate for unskilled workers which is the price of unskilled labor.
A price floor means that the price of a good or service cannot go lower than the regulated floor.
Governments put in place price floors in markets with inelastic demand inelastic demand inelastic demand is when the buyer s demand does not change as much as the price changes.
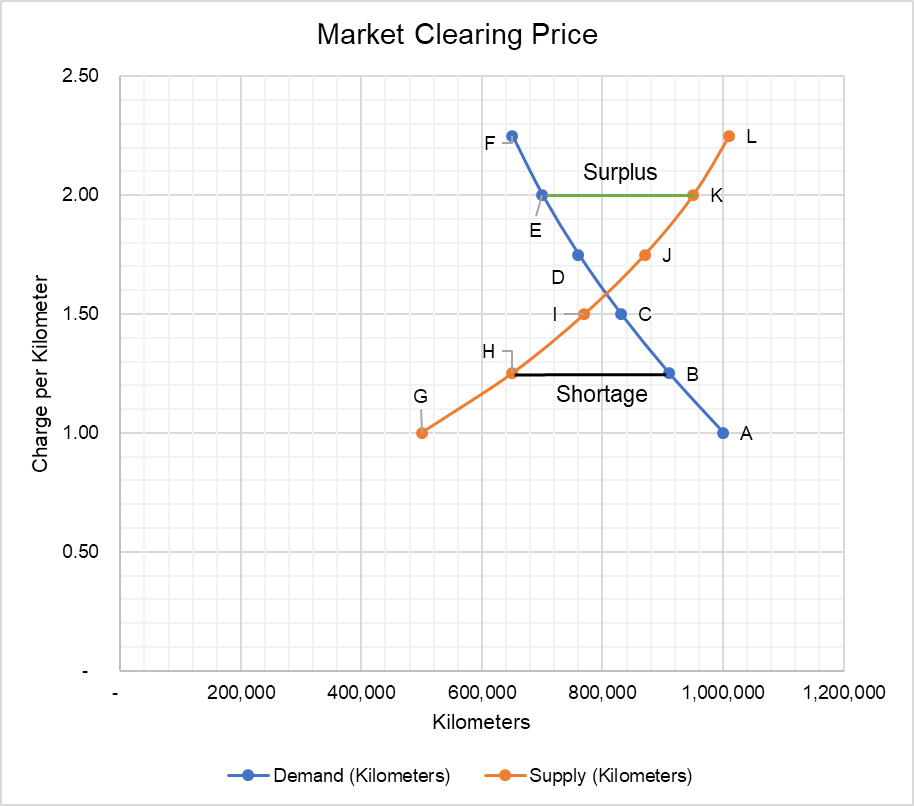
The effect of government interventions on surplus.
Taxes and perfectly inelastic demand.
In other words they do not change the equilibrium.
A minimum wage law is the most common and easily recognizable example of a price floor.
They simply set a price that limits what can be legally charged in the market.
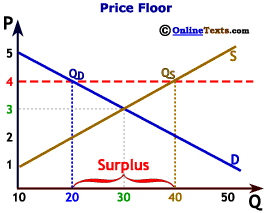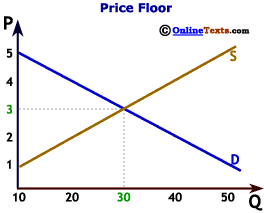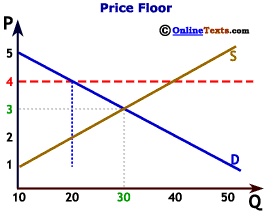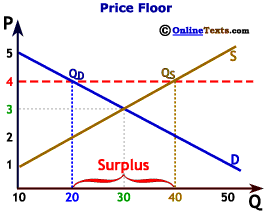
On the other hand since the price is higher than what it would be at equilibrium the suppliers producers are willing to supply more than the equilibrium quantity.
Taxation and dead weight loss.
A price floor is a minimum price enforced in a market by a government or self imposed by a group.
Do price ceilings and floors change demand or supply.
Price ceilings and price floors.
A price floor is the other common government policy to manipulate supply and demand opposite from a price ceiling.
The intersection of demand d and supply s would be at the equilibrium point e 0.
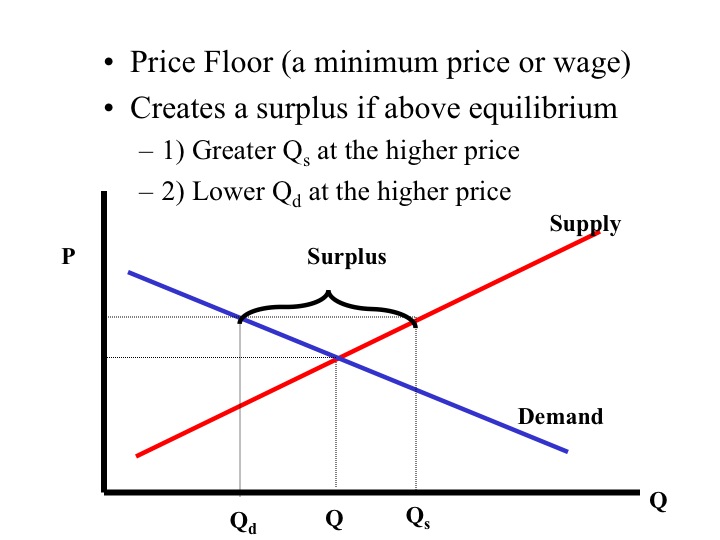
The result of the price floor is that the quantity supplied qs exceeds the quantity demanded qd.
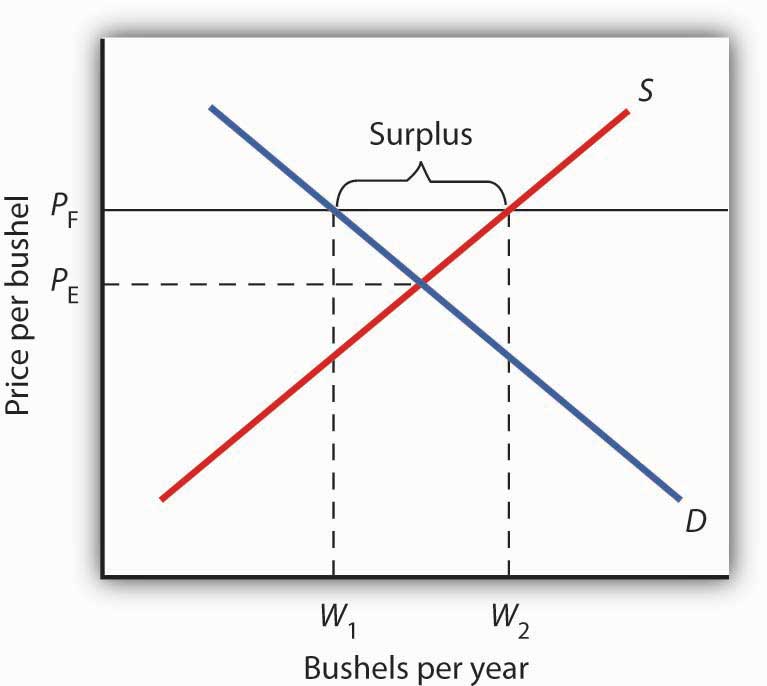
It tends to create a market surplus because the quantity supplied at the price floor is higher than the quantity demanded.
Price controls come in two flavors.